Current activities in the field of vehicle electrification
offer a great potential for contributing to climate change
mitigation by reducing anthropogenic CO2 emissions.
Beyond the environmental strain, there is also an
economic one. In 2017 the automotive sector accounted
for 4% of EU's GDP employing approximately 12 million
people in the manufacturing, sales, maintenance, and
transport domain.
It is therefore crucial for the European automotive
industry to exploit not only the environmental benefits,
but also the business opportunities which come from the
transition from conventional fuel powered to electrified
vehicles. In order to capture these opportunities, electric
vehicles must deliver better performance at a lower price,
overcoming the constraints that are currently limiting their
mass-market uptake. One major constraint is the limited
driving range compared to conventional vehicles due to
the limited battery capacity and high cost of the electric
energy storage systems.
The QUIET project aims at developing an improved and
energy efficient electric vehicle with increased driving
range under real-world driving conditions. This is achieved
by exploiting the synergies of a technology portfolio in the
areas of user-centric design with enhanced passenger
comfort and safety, lightweight materials with enhanced
thermal insulation properties, and an optimised vehicle
energy management.
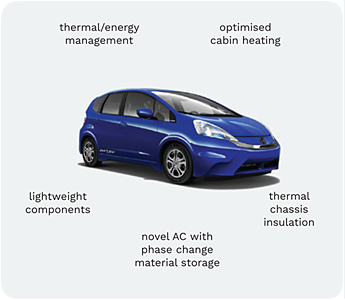 The developed technologies will be integrated and
qualified in a Honda B-segment electric vehicle validator.
Among these, a novel refrigerant for cooling, combined
with an energy-saving heat pump operation for heating,
advanced thermal storages based on phase change
materials, powerfilms for infrared radiative heating, and
materials for enhanced thermal insulation of the cabin
will be investigated. Further focus is put on lightweight
glasses and composites for windows and the chassis,
as well as light metal-aluminium or magnesium seat
components. Optimised energy management strategies,
such as pre-conditioning and zonal cooling/heating in
the passenger cabin as well as user-centric designed
cooling/heating modules will further enhance the thermal
performance of the vehicle. These strategies will be
seamlessly implemented in an intelligent vehicle control
unit enhanced by a novel Human Machine Interface,
which, beyond being intuitive and user friendly, will also
consider diverse users’ needs, accounting for gender and
ageing society aspects.
The developed technologies will be integrated and
qualified in a Honda B-segment electric vehicle validator.
Among these, a novel refrigerant for cooling, combined
with an energy-saving heat pump operation for heating,
advanced thermal storages based on phase change
materials, powerfilms for infrared radiative heating, and
materials for enhanced thermal insulation of the cabin
will be investigated. Further focus is put on lightweight
glasses and composites for windows and the chassis,
as well as light metal-aluminium or magnesium seat
components. Optimised energy management strategies,
such as pre-conditioning and zonal cooling/heating in
the passenger cabin as well as user-centric designed
cooling/heating modules will further enhance the thermal
performance of the vehicle. These strategies will be
seamlessly implemented in an intelligent vehicle control
unit enhanced by a novel Human Machine Interface,
which, beyond being intuitive and user friendly, will also
consider diverse users’ needs, accounting for gender and
ageing society aspects.
The objective of the QUIET project is to reduce the energy
needed for cooling and heating the cabin of an electric
vehicle under different driving conditions, by at least 30%
compared to the Honda baseline vehicle. Additionally, a
weight reduction of about 20% of vehicle components (e.g.
doors, windshields, seats, heating and air conditioning) is
addressed. These efforts will finally lead to a minimum of
25% driving range increase under both hot (+40°C) and
cold (-10°C) weather conditions
The QUIET project consortium involves a collaboration of 13 multi-disciplinary and complementary partners from industry and research originating from 6 different countries. All public deliverables and further information about QUIET are available at https://www.quiet-project.eu/.
Acknowledgement: The QUIET project has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No. 769826.