Page 32 - European Energy Innovation - winter 2018 publication
P. 32
32 Winter 2018 European Energy Innovation
ENERGY POVERTY
What consequences for
increasing levies on electricity?
By Sébastien Doligé, Senior Advisor Markets & Customers, Eurelectric
More and more consumers struggle to pay their energy bills and to heat or cool their homes.
Faced with this reality, European and national authorities must act. Consumers’ electricity bills
should stop being a vehicle for financing other – sometimes totally unrelated – policies.
Energy efficiency is key for
alleviating energy poverty. have recently made the headlines suppliers provide energy efficiency
Therefore, financing tools in several European countries, with advice, payment arrangements,
that leverage private suppliers being the main defenders. and appropriate debt management
However, reality shows that policy processes. Many suppliers have
investments should be chosen ahead costs and levies have been the also signed agreements with local
of regulating prices or taxes and main driver for higher households’ authorities and social services to
levies reflected through an increase electricity prices over the past support low income consumers and
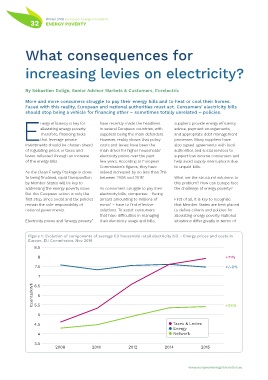
of the energy bills. few years. According to European help avoid supply interruptions due
Commission’s figures, they have to unpaid bills.
As the Clean Energy Package is close indeed increased by no less than 71%
to being finalised, rapid transposition between 2008 and 20151. What are the structural solutions to
by Member States will be key to this problem? How can Europe face
addressing the energy poverty issue. As consumers struggle to pay their the challenge of energy poverty?
But this European action is only the electricity bills, companies – facing
first step, since social and tax policies arrears amounting to millions of First of all, it is key to recognise
remain the sole responsibility of euros2 – have to find effective that Member States are best placed
national governments. solutions. To assist consumers to define criteria and policies for
that have difficulties in managing alleviating energy poverty. National
Electricity prices and “energy poverty” their electricity usage and bills, situations differ greatly in terms of
Figure 1: Evolution of components of average EU household retail electricity bill – Energy prices and costs in
Europe, EU Commission, Nov 2016
8.5
8 +71%
7.5 +/-0%
7
€cents/kWh 6.5
6
5.5 +26%
5
4.5 l Taxes & Levies
l Energy
4 l Network
3.5 2008 2010 2012 2014 2015
www.europeanenergyinnovation.eu